A patent is equivalent to an intangible asset of a company. For those engaged in the foreign trade industry, it is a means and a tool to occupy the market and attract target consumers.
Recently, there is a very eye-catching case in the patent circle of friends. One patent application of Intel is CN201210161092.2. The application date is December 1, 1995, and the authorization date is June 29, 2016. Authorization is only granted after 20 years of patent expiration. When the news came out, the people who had eaten melons said that they could not calmly face it. What happened?

Look at the timeline:
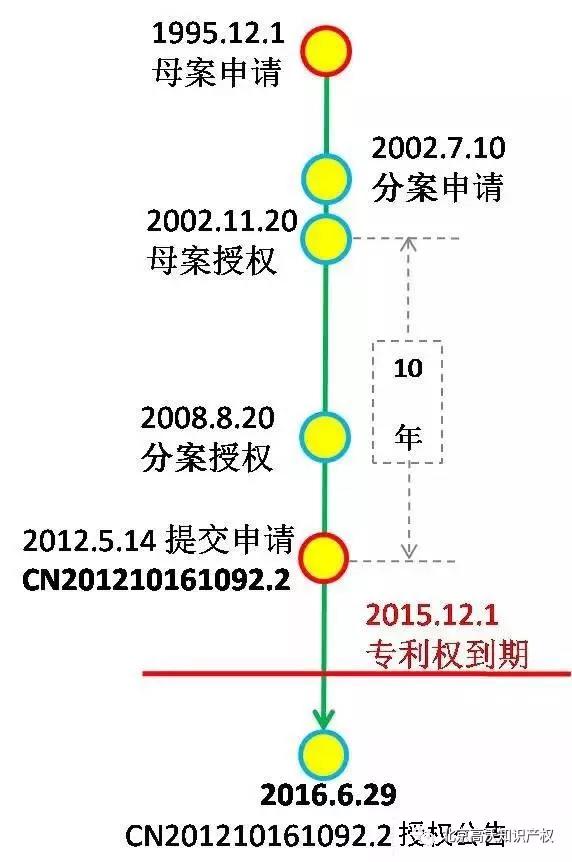
The application date of the applicant's original application (application number 95197430.0) was December 1, 1995. The case was granted a patent right on November 20, 2002, and the patent right expired on December 1, 2015. On July 2, 2002, the case was granted a patent on August 20, 2008, and the patent expired on December 1, 2015. However, the applicant Intel submitted a divisional application in 2007, the authorization time is July 4, 2012; then the applicant Intel submitted another divisional application on May 14, 2012 (application number 201210161092.2 ), authorized on June 29, 2016. That is to say, the division proposed in 2007 and the proposal in 2012 are authorized after the original application is authorized.
For a time, many people are not calm, nor do they understand. In fact, what is involved here is the knowledge of patent division.
Patent applications also have avatars. Article 42 of the Regulations for the Implementation of the Patent Law of the People's Republic of China states: If a patent application includes more than two inventions, utility models or designs, the applicant may, in Article 54 of these Rules. Before the expiration of the period specified in the first paragraph, a separate application shall be filed with the patent administration department under the State Council; however, if the patent application has been rejected, withdrawn or deemed to have been withdrawn, no divisional application may be filed. The conditions for submission of divisional applications are further regulated in the Patent Examination Guidelines.
So, what is the division strategy of the above-mentioned Intel for more than 20 years? Let us first review the relevant provisions of the Patent Examination Guidelines on the submission of divisional applications (Part I, Chapter 1, Section 5.1.1):
The applicant shall file a divisional application at the latest before the expiration of the two-month period (ie, the period for registration) from the date of receipt of the patent application by the Patent Office. After the expiration of the above period, or if the original application has been rejected, or the original application has been withdrawn, or the original application is deemed to have been withdrawn and has not been reinstated, it is generally not allowed to file a divisional application.
For the original application for which the examiner has issued a refusal decision, within three months from the date the applicant receives the refusal decision, the applicant may file a divisional application regardless of whether the applicant files a request for review; after the request for review and the decision for review During the period of dissatisfaction with the administrative proceedings, the applicant may also file a divisional application.
For an application that has been filed, the applicant needs to file a separate application for the divisional application, and the submission time of the divisional application submitted again should still be reviewed according to the original application. If the submission date of the division is not in conformity with the above provisions, no case will be scored.
However, due to the singularity of the divisional application, the applicant shall submit the application for division according to the reviewer's review opinion. For such exceptions, the applicant shall file a separate application for division, and shall submit a copy of the notice of review or the notice of division of the notice indicating the single defect.
The original meaning of the above provisions is that, under normal circumstances, the submission time of the first-generation divisional application should be that the parent case is not finalized, but the book stipulates that “the applicant has the singularity of the divisional application, and the applicant’s review opinion according to the examiner’s opinion In addition to the case where the divisional application is filed again, the original application (as the parent of the first-generation division) has been closed, but if the first-generation division is still closed, if the examiner is on the first generation If a notice of review or a division notice indicating a single defect is issued, the second-generation division may be submitted at any time during the first-generation division review process, and is not subject to the basis of the first-generation division. The time limit for the parent application is pending. At this point, it can be understood that the first-generation division became the parent of the second-generation division.
The original purpose of the division is to give a re-submission opportunity to an invention that does not have unity. This is also the most basic function of the division. However, the development of the patent industry today has given the meaning of a more divisional strategy.
Based on the current patent examination system, applicants can use the active divisional application to achieve some unexpected results. The agency's flexible use of the patent system can maximize the protection of the applicant's interests.

 News
News